Introduction
As the global environment faces unprecedented challenges, the preservation of biodiversity has become a critical concern. One of the innovative solutions to this pressing issue is the development of automated seed banks, powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics. These advanced technologies are not only enhancing the efficiency of seed conservation but also playing a pivotal role in safeguarding genetic diversity for future generations.
The Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, encompassing the diversity of species, ecosystems, and genetic variations. The significance of biodiversity cannot be overstated, as it underpins ecosystem stability, resilience, and the provision of essential services such as food security, clean water, and climate regulation. Unfortunately, human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change have led to a drastic decline in biodiversity, necessitating urgent action.
Understanding Automated Seed Banks
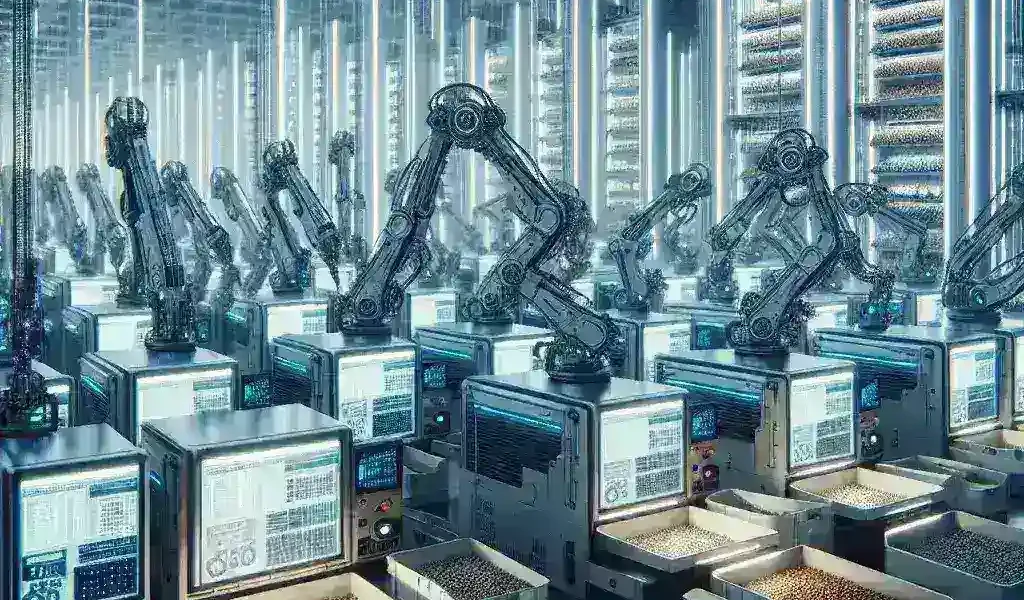
Automated seed banks are facilities designed to store seeds in controlled environments to maintain their viability over time. These seed banks utilize advanced technologies to ensure the preservation of plant species, especially those that are endangered or at risk of extinction. The integration of AI and robotics into seed bank operations is revolutionizing this crucial aspect of biodiversity conservation.
How AI Robotics Works in Seed Banks
AI robotics streamlines the seed banking process through automation and data analysis. Here are some key functionalities:
- Seed Collection: Robotics can automate the collection of seeds from various plant species, reducing human labor and minimizing the risk of contamination.
- Sorting and Processing: AI algorithms can analyze seed quality, ensuring only viable seeds are selected for storage. Robotics can also facilitate the sorting and packaging process.
- Environmental Control: Automated systems can monitor and adjust the storage conditions—such as temperature, humidity, and light—ensuring optimal conditions for seed preservation.
- Data Management: AI can analyze extensive data sets, including genetic information and historical data, to enhance seed bank management and facilitate research.
Historical Context of Seed Banks
The concept of seed banking is not new. The first seed banks were established in the early 20th century, with the Svalbard Global Seed Vault in Norway being one of the most well-known examples. However, traditional seed banks often face challenges such as inadequate storage conditions, limited resources, and the risks posed by natural disasters. The advent of AI and robotics offers a transformative approach to these challenges, elevating seed banking to new heights.
Future Predictions for AI-Driven Seed Banks
As technology continues to evolve, the future of automated seed banks looks promising. Here are some predictions:
- Increased Capacity: AI robotics will enable seed banks to expand their capacity, potentially storing millions of seed varieties.
- Enhanced Genetic Engineering: Advanced data analysis can assist researchers in identifying and engineering traits that enhance plant resilience to climate change.
- Global Collaboration: AI-driven platforms may facilitate international collaboration among scientists, allowing for a more comprehensive approach to biodiversity preservation.
Pros and Cons of Automated Seed Banks
While the advantages of using AI and robotics in seed banking are substantial, it is essential to consider potential drawbacks:
Pros:
- Efficiency: Automation significantly reduces the time and labor required for seed collection, processing, and storage.
- Accuracy: AI algorithms improve the selection and preservation of high-quality seeds, minimizing human error.
- Scalability: Automated systems can be expanded easily to accommodate growing demands for seed storage.
Cons:
- Initial Investment: The setup costs for AI and robotic systems can be high, posing a barrier for smaller organizations.
- Reliability on Technology: Over-reliance on technology may lead to vulnerabilities, especially if systems fail or become outdated.
Real-World Examples of AI Robotics in Seed Preservation
Several organizations are already harnessing AI robotics for seed preservation:
- The Millennium Seed Bank: Located in the UK, this facility employs robotic systems for efficient seed processing and long-term preservation.
- Future Farmers: A consortium employing AI to enhance seed selection processes for sustainable agriculture.
Cultural Relevance of Biodiversity Preservation
Preserving biodiversity is not just an ecological necessity; it is also a cultural imperative. Many indigenous communities depend on diverse plant species for their livelihoods and cultural practices. The integration of AI robotics into seed banking can help safeguard these cultural heritages by ensuring that vital plant species are preserved for future generations.
Statistics Highlighting the Need for Action
According to recent studies, approximately 1 million plant and animal species are currently at risk of extinction due to human activities. Furthermore, the loss of biodiversity can lead to a decrease in ecosystem services valued at trillions of dollars annually. These alarming statistics underline the urgency of implementing innovative solutions, like AI robotics in automated seed banks.
Expert Opinions on AI in Seed Banking
Leading experts in the field of conservation and technology emphasize the potential of AI-driven seed banks. Dr. Jane Goodall, a renowned primatologist and conservationist, states, “Harnessing technology to protect our planet’s flora is not just wise; it is essential for our survival. Automated seed banks can play a crucial role in conserving biodiversity for the future.”
Personal Anecdotes and Experiences
Many scientists and conservationists have shared their experiences working with automated seed banks. For instance, a researcher at the Svalbard Global Seed Vault noted how the implementation of robotics has markedly improved their operational efficiency, allowing them to focus more on research and less on manual labor.
Conclusion
The integration of AI robotics into automated seed banks presents a groundbreaking opportunity to enhance biodiversity preservation efforts. While challenges remain, the promise of this technology far outweighs the cons. By investing in AI-driven solutions, we can take significant steps toward ensuring a sustainable future for our planet’s diverse ecosystems.
Call to Action
As we stand on the brink of a new era in biodiversity preservation, it is imperative for policymakers, scientists, and communities to collaborate and invest in these innovative technologies. Together, we can build a future where biodiversity thrives, and the intricate web of life on Earth is maintained for generations to come.